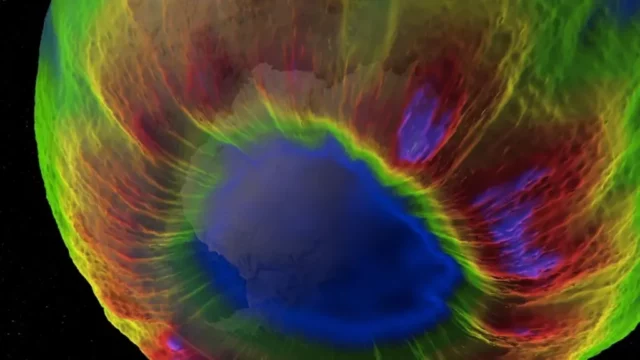
The Vital Role of the Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is our planet’s shield against the harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays of the Sun. Think of it as a protective blanket—without it, life as we know it would be drastically different. From the vibrant ecosystems of tropical forests to the expansive tundras, the ozone layer plays a crucial role in maintaining life by safeguarding living beings from excessive UV exposure. However, its importance is often overlooked until we face a crisis. In the late 20th century, scientists uncovered alarming evidence of a hole in this vital layer, a discovery that raised red flags around the globe.
Understanding Ozone Depletion and Holes
Every year, a troubling phenomenon occurs as the ozone layer weakens, particularly over polar regions. Factors like low temperatures and high humidity lead to chemical reactions that degrade ozone molecules, creating seasonal ozone holes. These holes vary in size and intensity, appearing to grow and shrink throughout the year. According to data from the World Meteorological Organization, the ozone hole over Antarctica can reach an area larger than North America, illustrating the seriousness of the issue.
Effects on Flora and Fauna
The consequences of ozone depletion reach far beyond the atmosphere. The ozone hole typically grows most significant from September to October, affecting a wide array of life. Plants, crucial to our oxygen supply and food chain, are especially vulnerable. Without adequate protection from UV rays, photosynthesis can be disrupted, leading to stunted growth or even species decline. Imagine a farmer noticing reduced crop yields year after year; this can directly impact food supplies and economic stability.
Challenges for Arctic Wildlife
In the Arctic, the situation is even more precarious. The intense UV rays can cause severe eye damage to wildlife, particularly during their breeding season in summer. Species such as seals and polar bears face increased risks, as their habitats are already threatened by climate change. Research indicates that as temperatures rise, events like forest fires release particles that not only worsen air quality but also catalyze destructive chemical reactions that further damage the ozone layer. It’s a vicious cycle that places immense stress on these vulnerable animals. For instance, a polar bear struggling to see due to UV-related eye damage might find hunting more difficult, affecting its survival.
What You Can Do
While the situation may seem dire, collective action can help mend the ozone layer. Here are some unique tips to contribute to this cause:
- Reduce chemical use: Opt for products that are low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and avoid aerosol sprays that can release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere.
- Embrace renewable energy: Shift towards solar or wind energy sources to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, which contribute to ozone layer depletion.
- Support sustainable practices: Advocate for and engage in agricultural practices that minimize chemical fertilizers and pesticides, helping to protect ecosystems.
The fight to protect the ozone layer is a shared responsibility. By raising awareness and taking proactive steps, we can diminish the risks associated with ozone depletion. After all, our planet’s health is intertwined with our well-being. Let’s make informed choices today for a more sustainable tomorrow!